Kanban is one of the most effective approaches to managing inventory and making the processes better. Kanban is a production system that was originally invented by Toyota and that has become a universal model to control the work visualization, inventory management, and smooth production flow. Be it a production facility or an organizational setting in the services industry, immobile knowledge of how Kanban performs and proper calculation of Kanban size will be a key to ensuring an optimal flow of supply chains.
What is Kanban ?
Kanban assists an organization to deal with flow of work and managing the inventory. Kanban, so far as Japanese is concerned, means signboard or visual signal. Kanban cards or signals can be physically used to initiate the action i-e the replenishment of materials, parts movement or initiation of production. The idea is to have an undisturbed flow of materials with minimal wastage of material and lead time.
A Kanban system usually includes cards, containers and a fixed number of items that each container can hold. After emptying a container, the Kanban card sticks to it states that the container has to be provided with replenishment. Such a pull-based system makes sure that production occurs only when there is actual demand, as opposed to the push systems that plan production based on estimates.
Why Kanban Matters in Lean Manufacturing ?
Kanban helps the Lean Manufacturing by eliminating waste (Muda), responding to customer demands and continuous improvement (kaizen). It assists in the accomplishment of:
- Reduced stocks
- Opened up visibility to loss
- Better inter-processing communication
- Swift reaction to the fluctuations in customer demand
- Improved lead time and excessive production
The critical issue in rolling out a successful Kanban system is the appropriate size of Kanban cards and this is also known as the number of Kanban cards.
How to Calculate Kanban Size ?
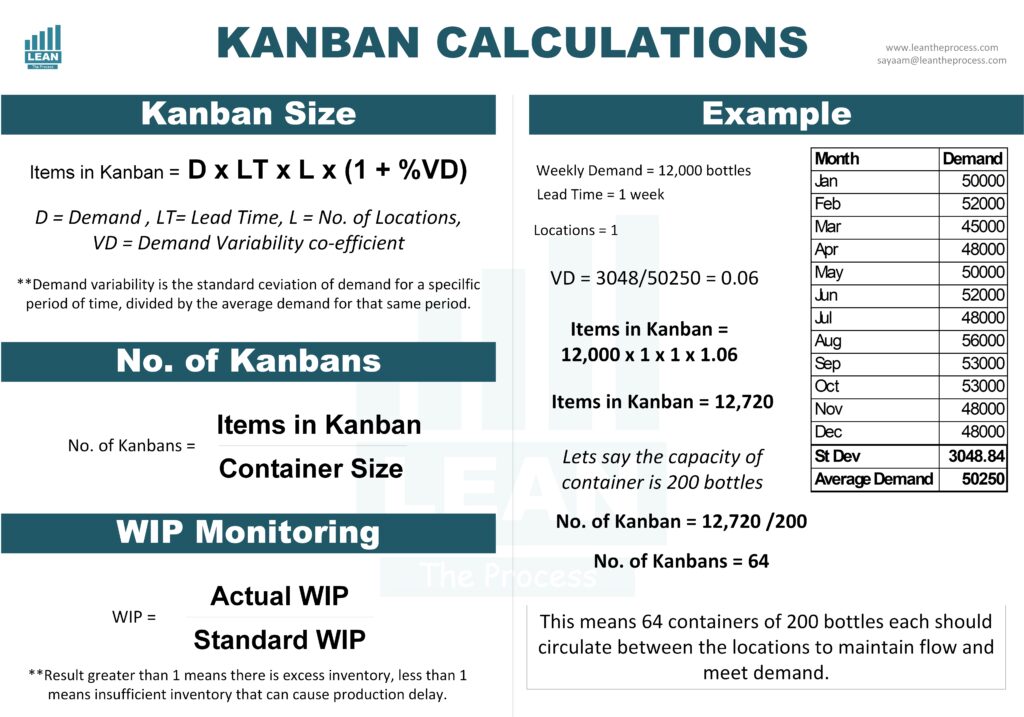
Calculating the correct Kanban size is critical for maintaining a smooth production flow without causing stockouts or excessive inventory. The general formula used to calculate the number of Kanban cards (or containers) required is:
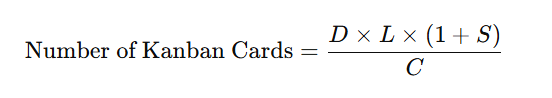
Where:
- D = Demand rate (units per period)
- L = Lead time (in the same time period as demand)
- S = Safety factor (to cover variability in demand or lead time)
- C = Container size (units per container)
Example
Suppose a company has:
- Weekly demand (D) = 12,000 bottles
- Lead time (L) = 1 week
- Safety factor (S) = 0.06 (or 6%)
- Container size (C) = 200 bottles
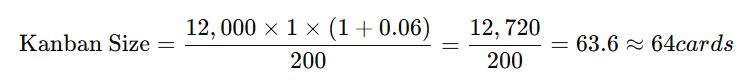
So, the company should maintain 64 Kanban cards in circulation to meet demand while accounting for variability.
Factors Effecting Kanban Size
The Kanban size is not static it depends on real-time factors such as:
- Changes in customer demand
- Variability in supplier lead times
- Shifts in production cycle time
- Inventory policy and buffer strategy
A well-tuned Kanban system requires regular review and adjustment of these factors to prevent overproduction or stockouts.
Kanban is also a mindset shift that emphasizes unending flow, eradication of waste and process control. Proper approach to the calculation of Kanban size allows you to make your production system work efficiently with the due proportion between the stock and the demand of customers. Through the adoption and improvement of the Kanban systems, organizations are in a position to convert their supply chains into perfect, quick responsive and waste free system.
